Earthquake Hazards: Tectonic Subsidence
Subsidence is the lowering of the ground surface. Tectonic subsidence is the lowering of the ground as a result of an earthquake.
While there are subsidence can occur as the result of different types of tectonic actions, generally tectonic subsidence happens when the vertical movement of ground causes nearby ground to lower in relation to it's previous location. This is what can happen with normal faults.
In a normal faulting zone, subsidence is evident from the creation of horsts and grabens, raised or lowered blocks of crust.
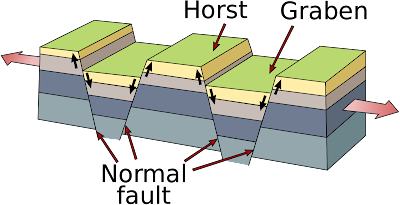 |
| Horst and graben along normal fault zone. USGS image, public domain. |
A pull-apart basin can be created in a strike-slip fault zone. Strike-slip faults are where the blocks of crust have faults that are vertical, or near vertical, and movement on the fault is usually sideways (horizontally). A pull-apart basin forms when opposing walls of the fault pull apart from each other, resulting in dropped ground.
Tectonic subsidence may also occur when loose sediments lose
their load-bearing strength (as in the case of liquefaction) and the ground
settles or slumps downward. For example, if an underlying layer of sediment
liquefies, the top layer could drop, even though objects on the surface may not
actually sink into the ground.
While tectonic subsidence can create foundation issues on structures in the affected zone, one of the greatest dangers of tectonic subsidence is in low-lying
areas near large bodies of water, such as coastal areas or lakeshores. If the
area drops below the water level, permanent flooding may result.

Comments
Post a Comment